Overview
In fourth grade, students in SFUSD engage in 50-60 minutes of daily math instruction. Math instruction supports students in building agency and supports their identities as mathematicians. Math lessons provide both concrete and conceptual understanding for students by giving them opportunities to deepen their understanding of concepts through play and exploration. By the end of the year, Grade 4 students can fluently add and subtract within 1,000,000.

During math instruction, students are engaged in a number of instructional contexts and routines: math talks and counting routines. Math talks feature flexibility with numbers and developing an understanding of the base 10 system. Examples include describing visual arrangements of objects using math expressions, or flexibly adding and subtracting numbers up to a thousand by putting together and pulling apart each addend using place value understanding. In addition, engaging in collaborative tasks and games will result in joyful math learners.
Priority Standards Link to this section
What students will know, what students will do, and what thinking skills students will develop to apply and transfer mathematical understandings that endure within the discipline, leverage deeper understandings, and/or support readiness for success at the next grade level.
In Fourth Grade focus on these critical areas:

Developing Understanding & Fluency with Multi-Digit Multiplication, and Developing Understanding of Dividing to Find Quotients Involving Multi-Digit Dividends

Developing an Understanding of Fraction Equivalence, Addition & Subtraction of Fractions with Like Denominators, and Multiplication of Fractions by Whole Numbers

Understanding That Geometric Figures Can Be Analyzed & Classified Based on Their Properties, Such as Having Parallel Sides, Perpendicular Sides, Particular Angle Measures, & Symmetry
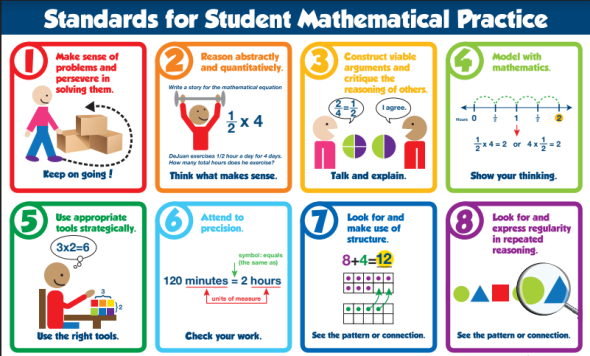
Behaviors of Mathematicians
- Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
- Reason abstractly and quantitatively
- Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others
- Model with mathematics
- Use appropriate tools strategically
- Attend to precision
- Look for and make use of structure
- Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Instruction: Signature Elements Link to this section
Below are signature elements of SFUSD Math instruction that students should experience regularly throughout Kindergarten as they develop as mathematicians.
Math Norms
Class norms help students, and give them opportunities to be accountable to the community and to act on the prosocial values of responsibility, respect, fairness, caring, and helpfulness. They support equitable participation, engagement with the practices of doing math, and the establishment of a positive classroom climate. Establish class norms at the beginning of the school year and continue to reinforce them every day.
Math Talks
Math Talks are teacher-led, student-centered techniques for building math thinking and academic discourse. They allow for multiple entry points and encourage students to value the thinking of others so that they can build a better understanding of their own thinking. Math Talks support students in developing their mental math skills.
Three Read Protocol
The Three Read Protocol is one way to do a close read of a complex math word problem or task. This strategy includes reading a math scenario three times with a different goal each time. The first read is to understand the context. The second read is to understand the mathematics. The third read is to elicit inquiry questions based on the scenario.

Groupwork Feedback
Groupwork feedback is a strategy to publicly recognize the class norms and math focus of students as they work in groups. Group work is loosely defined to include partners, trios, or larger group sizes. The teacher takes public notes about the quality of the group work and the quality of the mathematical discussions. This feedback should focus on the specific nature of groupwork interactions as well as target mathematics of the lesson rather than general positive reinforcement.

Routines
Set up strong daily routines at the beginning of the year. These routines can be part of your formal math block or during a separate time of the day and should last 10–15 minutes. Certain routines can be incorporated into transitional periods (as an example: when lining-up students can practice a counting routine. NOTE: Counting routines can be used kindergarten through 5th grade). Depending on the particular focus, each routine should be done daily, weekly, or monthly.
Materials
Below are items you should have to support your students' Math instruction. If you are missing anything from the list, please first contact your site administrator or designated support. If they are unable to resolve the issue promptly, please contact your site’s liaison from the SFUSD Math Team.
SFUSD Math Student Classwork and Homework booklets are centrally printed and provided by the SFUSD Math Department; the booklets are printed in English, Spanish, and Chinese. Here are PDFs for 4th Grade Student Pages (Grade 4) and 4th/5th Combination Grade Student Pages (Grade 4-5).
Manipulatives have been provided to each site and should remain with the classroom. Here is a linked list Full SFUSD Math Manipulative List (3_20).pdf of manipulatives for each grade Pre-Kindergarten through Grade 5.
Units
Unit Design
SFUSD units are designed around four tasks. These tasks offer all students opportunities to engage in meaningful and rigorous mathematics that allow for the development of the Standards for Mathematical Practice. They give information about how students are learning the core concepts and skills of the unit.
All tasks are used for formative assessment—gathering information about what students know and are able to do—but they are not tests. The Entry, Apprentice, and Expert Tasks allow for student collaboration and individual accountability without being graded based on an expectation of mastery. The Milestone Task can be used as an individual assessment for grading students.
 |
|---|
- Entry Task: What do you already know?
- Apprentice Task: What sense are you making of what you are learning?
- Expert Task: How can you apply what you have learned so far to a new situation?
- Milestone Task: Did you learn what was expected of you from this unit?
Units
| Unit | Description | Orientation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| The first week of school is focused on setting up the classroom culture for the year and developing routines that support the development of the Standards for Mathematical Practice. You will get to know your students, and students will get to know themselves as math learners. | |||
| The base-10 place value number system is an efficient way to represent numbers in writing and allows for use of efficient algorithms when adding or subtracting large numbers. | Unit 4.1 Orientation | ||
| Multiplicative comparison describes how many times as much or as many one number is when compared to another. | Unit 4.2 Orientation | ||
| Multiplication and division are inverse operations that can be represented with a variety of models that depend on how the context is being interpreted. | Unit 4.3 Orientation | ||
| One whole can be partitioned into tenths and hundredths and expressed in decimal or fraction form. These decimals and fractions can be compared to each other as well as used to solve real-world problems. | Unit 4.4 Orientation | ||
|
|
Fractions are composed of smaller units that can be added, subtracted, and multiplied by joining or separating them. | Unit 4.5 Orientation | |
|
|
Numbers can be classified as prime or composite and can be expressed as a product of their factors or as a factor of their multiples. | Unit 4.6 Orientation | |
| Measurement is a comparison of an attribute of something to a predetermined unit that has the same attribute, such as length to length or weight to weight. Measurement units can be decomposed into smaller units of equal size and used interchangeably. | Unit 4.7 Orientation | ||
| Polygons can be classified by attributes such as the presence or absence of parallel and perpendicular lines, angle measures, and lines of symmetry. | Unit 4.8 Orientation | ||
| A pattern has a core that repeats in predictable ways and can be generalized mathematically. | Unit 4.9 Orientation |
Lesson Structure and Core Math
|
LAUNCH |
The launch of a lesson or task is a brief hook that might relate to previous learning, establish an inquiry question, or connect to real-world situations or interests. It will also support students to understand what is being asked of them, which may include guidance on the use of materials such as manipulatives. |
|
Key Questions How can you connect to students' interests/lives (hook)? |
|
|
EXPLORE |
During the explore part of a lesson or task, students carry the cognitive load. They are experimenting together with number and shape to develop, deepen, or secure their mathematical understandings. They represent their thinking with numbers, pictures, words, and visual representations such as ten frames or number lines. They are talking throughout this part of the lesson, and building on each other’s ideas and questions. The explore often includes a math game. |
|
Key Questions What are students doing? What work do you want to highlight? What does their work show about what they understand? What language are the students using to describe their work? |
|
|
SUMMARIZE |
During the summarize part of a lesson or task, the teacher facilitates a conversation where students share what they have learned related to the core math. They notice and name similarities, differences, or connections across several different pieces of math work. A summary often, but not always, includes routines for consolidation of learning, such as a gallery walk or individual reflection in a notebook. |
|
Key Questions How will you sequence the work to elicit peer-to-peer academic discourse? What questions or prompts might you use? How will you connect different pieces of work to each other? How will you connect the work to the core math? |
Planning Guide
4th Grade Planning Calendar
4th/5th Grade Planning Calendar
This calendar is intended as an instructional guide to help with year-long planning. There is no expectation that you teach a particular lesson on a particular day. Each unit is set within a “window” of time that gives you some flexibility.
Reflection Questions Link to this section
- How are students' developmental needs, communities, and experiences being reflected and honored, or how could they be?
- What opportunities do you see for developing equitable access & demand, inquiry, collaboration, and assessment for learning?
- What are the implications for your own practice? What strengths can you build upon? What will you do first?
Want More?
Standards
More Resources
- The SFUSD Math Curriculum Grade 4 Overview includes the priority standards, the scope and sequence of units and standards, the unit design, class norms, key instructional strategies, and icons used throughout the curriculum to support planning.
- Assessment resources (in addition to the embedded formative assessment in the Core Curriculum)
Contact the Math Team:
This page was last updated on May 18, 2023

